
John P. DeLong, James L. Van, Zeina Al-Ameeli, Irina V. Agarkova and David D. Dunigan, ‘The consumption of viruses returns vitality to meals chains’, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, December 27, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.221500012
At varied peaks of the COVID-19 pandemic, viruses have had a repute as destroyers of public well being methods and human lives. They have a peculiar biology — whereas inert outdoors a residing physique , however inside, they hijack the mobile equipment to feed, replicate and unfold. This affiliation with illness and dying has come to outline their type within the public creativeness, redeemed not even by the truth that there are different microbes that destroy viruses. But a brand new examine, published on December 27 by researchers on the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, provides to upend this.
The authors of the examine have reported {that a} explicit genus of plankton can devour viruses in addition to “develop and divide given solely viruses to eat”. We already know of different cells that may ‘devour’ viruses in an effort to destroy them — such because the macrophage cells of the human immune system.
The distinction lies in with the ability to ‘eat’ viruses to fulfil one’s organic imperatives.
Plankton of the genus Halteria, they declare to have discovered, can every devour 10,000 to 1,000,000 virus particles a day, enhance their inhabitants utilizing the metabolised vitality, and supply extra meals for the zooplanktons that devour the Halteria. This may very well be important for the marine meals chain.
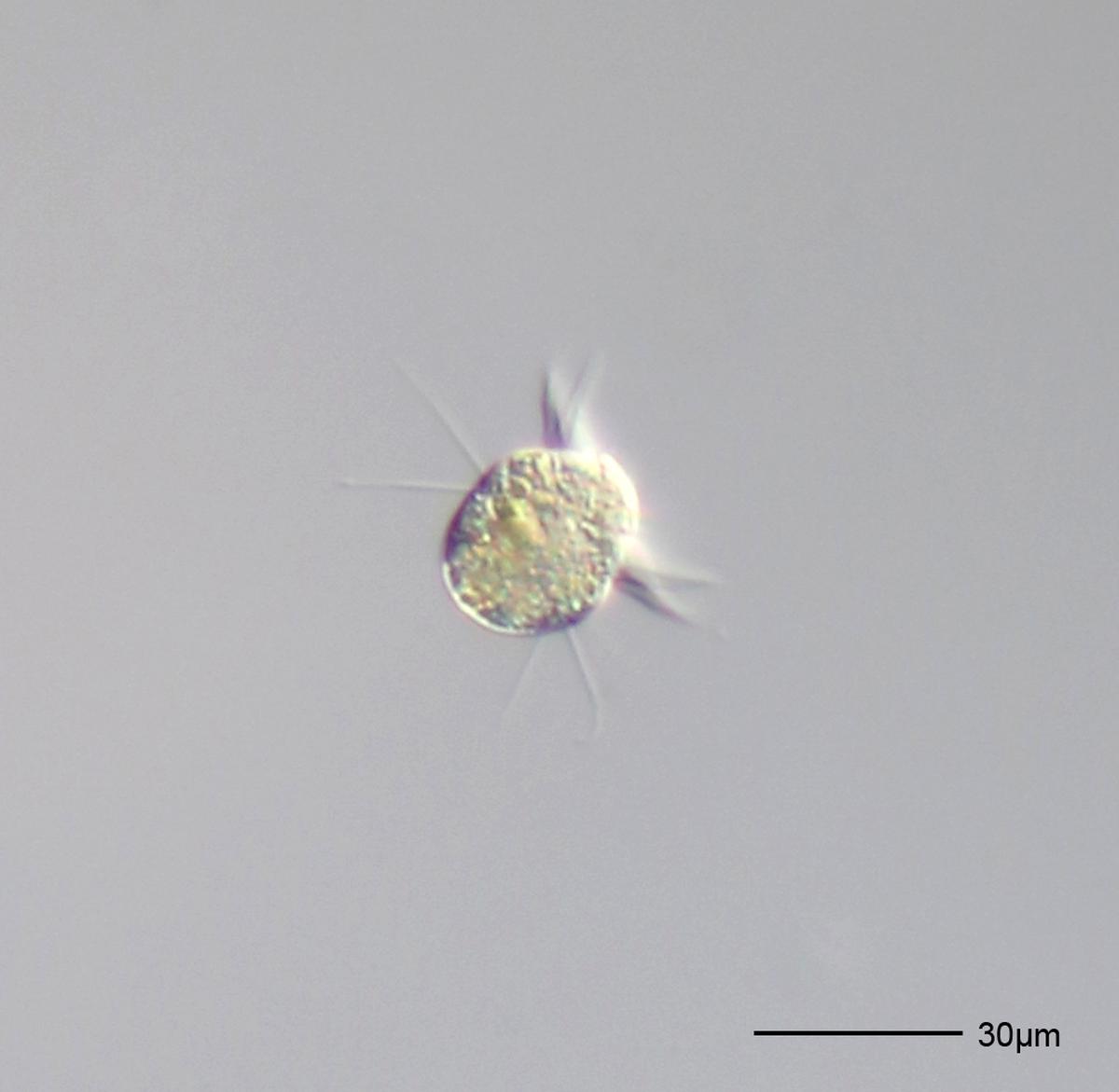

Halteria grandinella.
| Photo Credit:
Picturepest/Flickr
What are plankton?
Plankton are microscopic organisms that may solely transfer with a present. They don’t have any amenities to actively propel themselves. Halteria plankton are ciliates, that means they’ve hair-like constructions known as cilia on their floor. Sometimes they will beat a few of these cilia to leap quick distances, however not typically because it they will’t do that actually because it requires an excessive amount of vitality.
What do plankton do within the meals chain?
A kind of plankton — the phytoplankton — is discovered nearer the floor of many water our bodies. It is an autotroph, which suggests it will possibly make its personal meals which it does by consuming carbon dioxide, amongst different compounds, by means of photosynthesis. Small fish and bigger plankton known as zooplankton eat phytoplankton for his or her diet; they’re in flip eaten by bigger fish, and so forth.
When phytoplankton die, they drift round the place they’re, changing into a part of a coastal nutrient cycle, or they drift down in the direction of the seafloor, the place they decompose. Their constituents then grow to be obtainable for microbes or are sequestered into the seafloor.
So, phytoplankton deliver carbon and different vitamins from the ambiance and sea floor all the way down to the seafloor and assist replenish the meals chain (and likewise ‘entice’ carbon into their very own our bodies and as sediments). They are joined by micro organism that make their very own meals by oxidising sulphur, iron or hydrogen, in a course of known as chemosynthesis.
The function of Halteria
Halteria plankton are present in giant numbers in freshwater our bodies. They are heterotrophs that means they will’t produce their very own meals. Instead, they’re well-known bacterivores — they devour micro organism to energy themselves.
In the phrases of a noted 1999 paper, viruses “short-circuit” the method of vitamins shifting up the meals chain. They infect and kill each micro organism and plankton, releasing natural matter that dissolves within the water. Note that scientists have modelled this ‘viral shunt’ and studied it within the lab; investigations of its real-world impact are ongoing.
In the brand new examine’s paper, the authors wrote that by additionally consuming viruses for diet, Halteria plankton can get better the vitamins misplaced within the viral shunt and produce them again into the meals chain. “This circulate would rely on virion measurement and dietary content material, which varies amongst strains,” they added, “however it’s already clear that viruses of a variety of sizes might be taken up”.
Redemption for viruses?
Viruses are the single-most populous life-form on Earth; their cumulative biomass outweighs that of humans by an element of 10^10. In 2020, Curtis Suttle, a co-author of the 1999 paper, known as them “fantastic nutritional sources”.
The discovering wasn’t sudden. In 2020, a bunch from the U.S. and Spain published a paper after 10 years of data-taking and examine, positing that some protists (eukaryotes that aren’t crops, animals or fungi; eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have nuclei) is likely to be munching on viruses. They wrote that their findings “point out that the viral shunt is complemented by a viral hyperlink within the marine microbial meals internet”.
There have been papers discussing this hyperlink since at least 1992.
In the brand new examine, the researchers discovered that Halteria plankton diminished the inhabitants of chloroviruses ‘fed’ to them whereas rising their very own numbers — whereas Paramecium ciliates consumed the chloroviruses however didn’t proliferate. That is, to cite from their paper, “not all ciliates can develop on chloroviruses in these situations, even once they devour them”.
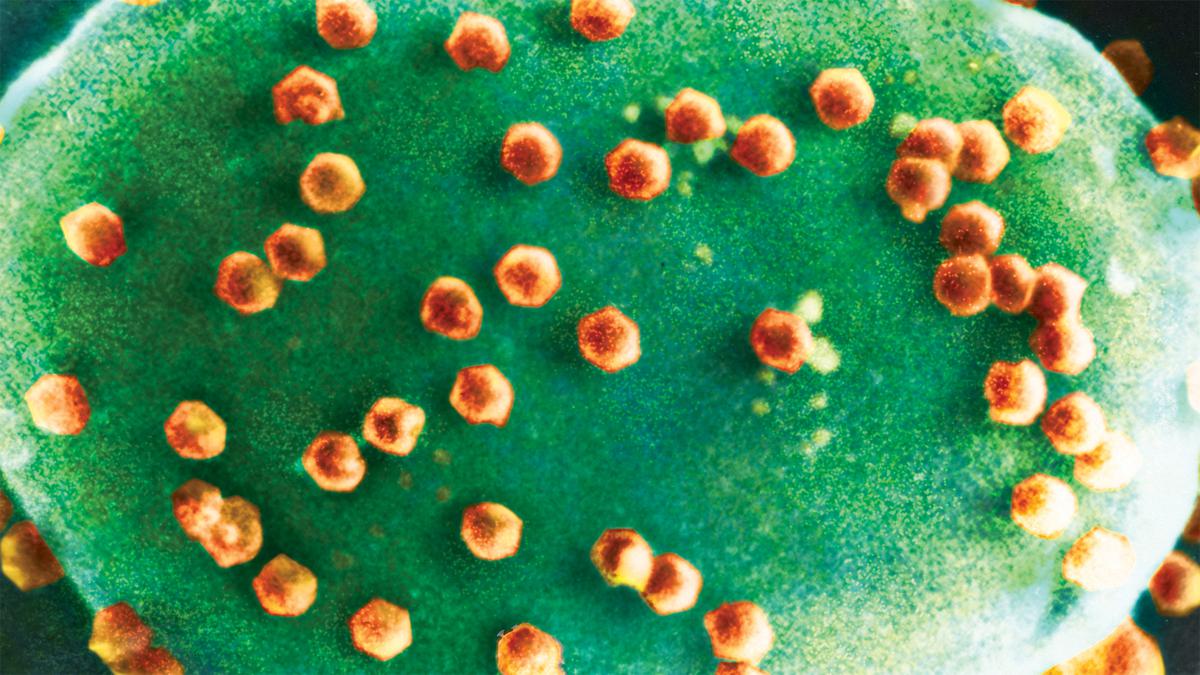
Chlorovirus particles on algae.
| Photo Credit:
Kit Lee and Angie Fox/University of Nebraska-Lincoln
Second, because the inhabitants of viruses and Halteria modified over the course of their interplay (within the lab), the researchers used a modelling instrument to grasp in the event that they match what we already learn about predator-prey interactions within the wild. The mannequin indicated that they did, however John DeLong, a biologist and the lead researcher, stated in a press release: “Now, we now have to go discover out if that is true in nature.”
DeLong et al. additionally wrote that they don’t but know the way Halteria feeding on viruses might have affected viral evolution.
https://news.google.com/__i/rss/rd/articles/CBMihwFodHRwczovL3d3dy50aGVoaW5kdS5jb20vc2NpLXRlY2gvc2NpZW5jZS92aXJhbC1udXRyaXRpb24tbmV3LXN0dWR5LXJldmVhbHMtbWljcm9iZXMtbm91cmlzaGVkLWJ5LWNvbnN1bWluZy12aXJ1c2VzL2FydGljbGU2NjM5NzI0MC5lY2XSAYwBaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cudGhlaGluZHUuY29tL3NjaS10ZWNoL3NjaWVuY2UvdmlyYWwtbnV0cml0aW9uLW5ldy1zdHVkeS1yZXZlYWxzLW1pY3JvYmVzLW5vdXJpc2hlZC1ieS1jb25zdW1pbmctdmlydXNlcy9hcnRpY2xlNjYzOTcyNDAuZWNlL2FtcC8?oc=5



